
#DEBIT CREDIT ACCOUNTING CHART PLUS#
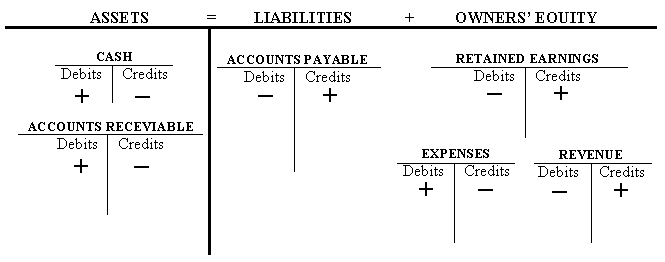
The upper section reads, from left to right, Assets equal Liabilities plus Equity. ReturnĪ representation of the expanded accounting equation divided into an upper and lower section. The space to the right of the vertical line is labeled Credit. The space to the left of the vertical line is labeled Debit. There is a short vertical line extending below the center of the horizontal line. There is a horizontal line across the center, above which is the label Account Title (such as Cash or Accounts Payable). Table 1.1 shows the normal balances and increases for each account type.Ī representation of a T-account. Since liabilities, equity (such as common stock), and revenues increase with a credit, their “normal” balance is a credit. Dividends paid to shareholders also have a normal balance that is a debit entry. As assets and expenses increase on the debit side, their normal balance is a debit. The normal balance is the expected balance each account type maintains, which is the side that increases. This becomes easier to understand as you become familiar with the normal balance of an account. This is also true of Common Stock and Revenues accounts. Liabilities increase on the credit side and decrease on the debit side. This is also true of Dividends and Expenses accounts. Source: Openstax CC BY NC-SA Long DescriptionĪs we can see from this expanded accounting equation, Assets accounts increase on the debit side and decrease on the credit side. We can illustrate each account type and its corresponding debit and credit effects in the form of an expanded accounting equation.įigure 1.5 A representation of the expanded accounting equation. Depending on the account type, the sides that increase and decrease may vary. You will often see the terms debit and credit represented in shorthand, written as DR or dr and CR or cr, respectively.

The ending account balance is found by calculating the difference between debits and credits for each account. One side of each account will increase and the other side will decrease. A credit records financial information on the right side of an account. Source: Openstax CC BY NC-SA Long DescriptionĪ debit records financial information on the left side of each account. A T-account is called a “T-account” because it looks like a “T,” as you can see with the T-account shown here.įigure 1.4 A representation of a T-account. This graphic representation of a general ledger account is known as a T-account. Each account can be represented visually by splitting the account into left and right sides as shown.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
